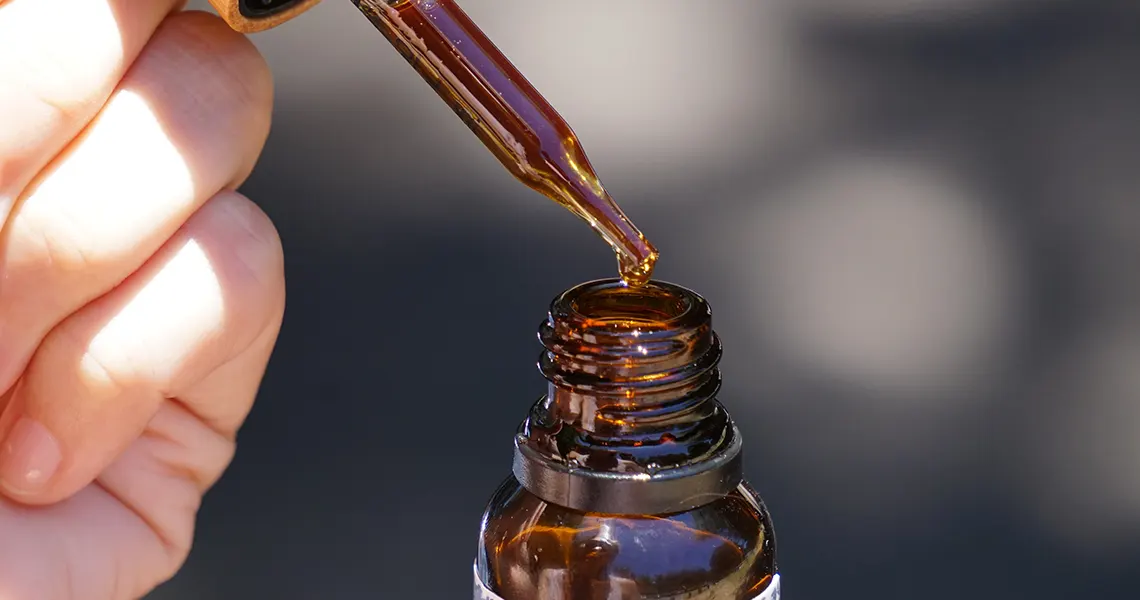

How is CBD oil taken?
CBD, or cannabidiol, is an alternative, plant-based treatment that comes in many forms. These include CBD oils, tinctures, edibles and creams. Each one operates fairly similarly and has similar contents, but they’re administered in different ways.
The main caveat is our lack of knowledge. Numerous studies have pinpointed potential therapeutic benefits. The issue here is that these studies have also delivered contradictory or hugely varying results. There are so many potential grounds to cover with CBD research that it, being a new field, will take years to understand in a more comprehensive way.
A few basics to understand about taking CBD oil:
- it’s more effective in treating symptoms than conditions
- the appropriate dose is dependent on various factors
- certain CBD products contain the psychoactive compound THC
- it won’t be an effective treatment for everybody.
You’ll also need to know how to access CBD legally, what kinds of oils are available and what kinds of products to avoid.
The most important step in taking cannabidiol is to discuss it with your doctor. They’ll need to consider your medical history and more to help identify whether the plant compound is an appropriate treatment.
What’s in CBD oil?

CBD a natural compound produced from the cannabis and hemp plants. Cannabidiol, along with THC, has become popular for its potential medical benefits. CBD is taken from resins produced by the leaves, stems and stalks of the plant.
They’re extracted using specialised equipment and techniques based around superheating carbon dioxide, using alcohol as a solvent and more.
To create CBD oil, the extract is added to a carrier oil. That could be hemp seed oil, olive oil or others. These are packaged in bottles and fitted with droppers the same way eye drops are.
It gets a little more complicated looking at the types of oils available. They are:
- full-spectrum
- broad-spectrum
- isolates
Each one is categorised by the hemp or cannabis compounds the oil contains, other than CBD. The most notable difference would be the inclusion of THC. Full-spectrum and broad-spectrum CBD both contain THC. The former at up to 0.3% and the latter in only trace amounts.
That’s important because people can react very differently to THC compared to cannabidiol. For starters, THC can induce a ‘high.’
Does CBD oil work?
This part is a little more difficult to describe. As we’ve hinted at, we don’t fully understand cannabidiol. That goes for both its potential benefits and side effects.
Our scientific understanding of CBD is based on how it interacts with the endocannabinoid system.
The belief is that cannabidiol assists this system with its goal of maintaining balance in the body. The endocannabinoid system delivers messages from the brain to the nervous system and causes action in cells throughout our body.
These affect and contribute to:
- digestion and immune response
- pain and inflammation reduction
- learning and memory
- sleep
- body temperature.
It’s possible that by engaging with this system cannabidiol may present numerous therapeutic benefits. Science has not confirmed this however and it will take much more research to get the full picture of how cannabidiol functions.
Cannabidiol also has its potential negative side effects. They are thought to be mostly mild but can differ from person to person. The most significant are anxiety, nausea, headaches and dry mouth.
Regardless, most research points towards CBD being safe for human consumption.
How do I take CBD oil?
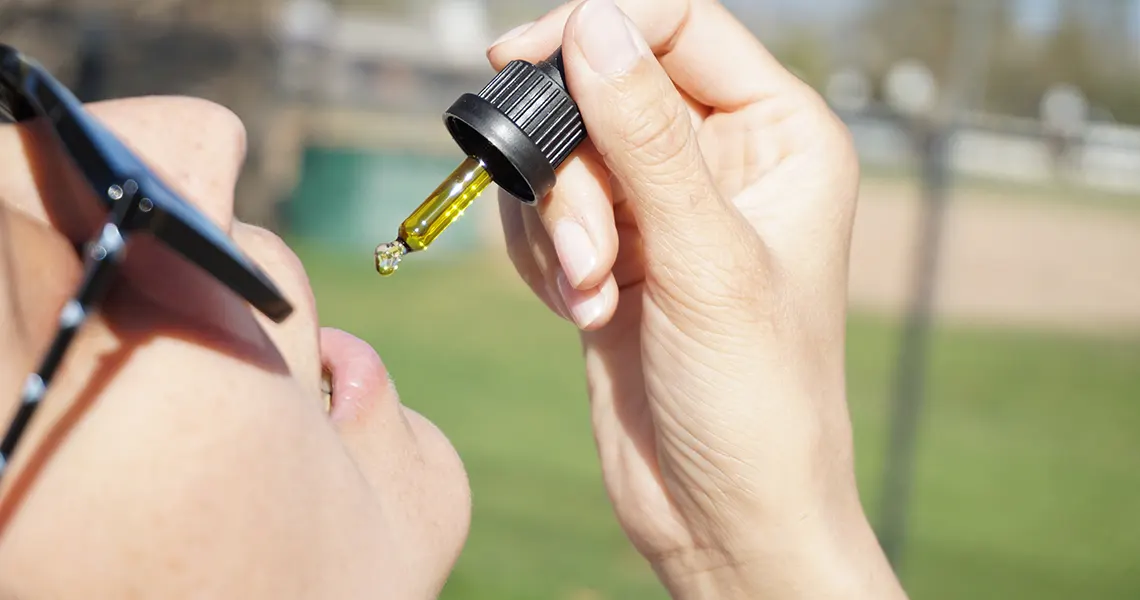

CBD oils are taken in drops. Generally sublingually (under the tongue), though they can also be mixed into food and drink. Oils are popular both because they take effect relatively quickly and because the droplets make it easy to measure your preferred or required dosage.
The sublingual approach is what allows the compound to kick in quickly. The underside of your tongue is lined with blood vessels. These absorb CBD and deliver it to the bloodstream, bypassing the digestive system.
From there, it should take around 15 – 30 minutes to settle in.
Edibles can take twice that amount of time, if not more, while vapes are inherently unhealthy and topical CBD creams only affect the applied area.
There are a few important factors to consider when deciding on dosage:
- the correct dosage is different for everybody
- oils tend to contain around 15 – 20 mg of CBD
- it’s dependent on your age, weight, height, body fat percentage and more.
These are all points to discuss with your doctor. They’ll answer want to carefully consider your medical history, as well as any other medications you may currently be on.
Keep in mind that cannabidiol is only available via prescription and that many products available online are unregulated. These present far more potential health risks.
The gist of taking CBD oil
To summarise, CBD oil is taken under the tongue. It takes 15 – 30 minutes to feel the effects but anyone considering plant-based treatments should also be sure to discuss usage in-depth with their doctor before committing to regularly taking cannabidiol.
Keep in mind that, though positive indications of CBD’s benefits exist, it will take years of additional research for us to more freely recommend the treatment.
You should also discuss THC content and prepare for the potential negative side effects. Just remember that these are considered mild and that CBD is thought by science to be safe for consumption. However careful consideration must be taken before choosing CBD as a treatment option.
